‘Market-implied estimates may be exaggerating rate-cut potential before year-end’
Author of the article:
Bloomberg News
Denitsa Tsekova
Published Apr 03, 2023 • Last updated 3 days ago • 4 minute read
Traders work on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange. Photo by Brendan McDermid/Reuters files Optimism about imminent rate cuts is stirring animal spirits and unease in equal measure at the end of a turbulent quarter in markets.
Advertisement 2 This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
THIS CONTENT IS RESERVED FOR SUBSCRIBERS ONLY Subscribe now to read the latest news in your city and across Canada.
Unlimited online access to articles from across Canada with one account Get exclusive access to the National Post ePaper, an electronic replica of the print edition that you can share, download and comment on Enjoy insights and behind-the-scenes analysis from our award-winning journalists Support local journalists and the next generation of journalists Daily puzzles including the New York Times Crossword SUBSCRIBE TO UNLOCK MORE ARTICLES Subscribe now to read the latest news in your city and across Canada.
Unlimited online access to articles from across Canada with one account Get exclusive access to the National Post ePaper, an electronic replica of the print edition that you can share, download and comment on Enjoy insights and behind-the-scenes analysis from our award-winning journalists Support local journalists and the next generation of journalists Daily puzzles including the New York Times Crossword REGISTER TO UNLOCK MORE ARTICLES Create an account or sign in to continue with your reading experience.
Access articles from across Canada with one account Share your thoughts and join the conversation in the comments Enjoy additional articles per month Get email updates from your favourite authors Prominent money managers have stopped chasing the latest stock rally, reasoning that expectations for easier United States Federal Reserve monetary policy are overblown with inflation still running hot. Should any rate cuts come, they would be intended to halt an economic downturn that also would bode poorly for equity returns, their thinking goes.
FP Investor Canada’s best source for investing news, analysis, and insight on investment strategies, stocks and more.
By clicking on the sign up button you consent to receive the above newsletter from Postmedia Network Inc. You may unsubscribe any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link at the bottom of our emails or any newsletter. Postmedia Network Inc. | 365 Bloor Street East, Toronto, Ontario, M4W 3L4 | 416-383-2300
Barclays Wealth Management just closed out an overweight position on developed market stocks two weeks after initiating it. Legal & General Group PLC, which manages US$1.4 trillion, has cut its equity exposure down to the biggest underweight since the pandemic, concluding that the hit from aggressive tightening will continue to play out on the U.S. economy for months to come. After the bank turmoil this month, asset managers shifted their stock exposure from close to neutral to a level halfway toward historically low underweight measures, according to Deutsche Bank AG.
Advertisement 3 This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
“Market-implied estimates may be exaggerating rate-cut potential before year-end,” said William Hobbs, chief investment officer at Barclays Wealth Management, who favours defensive positioning.
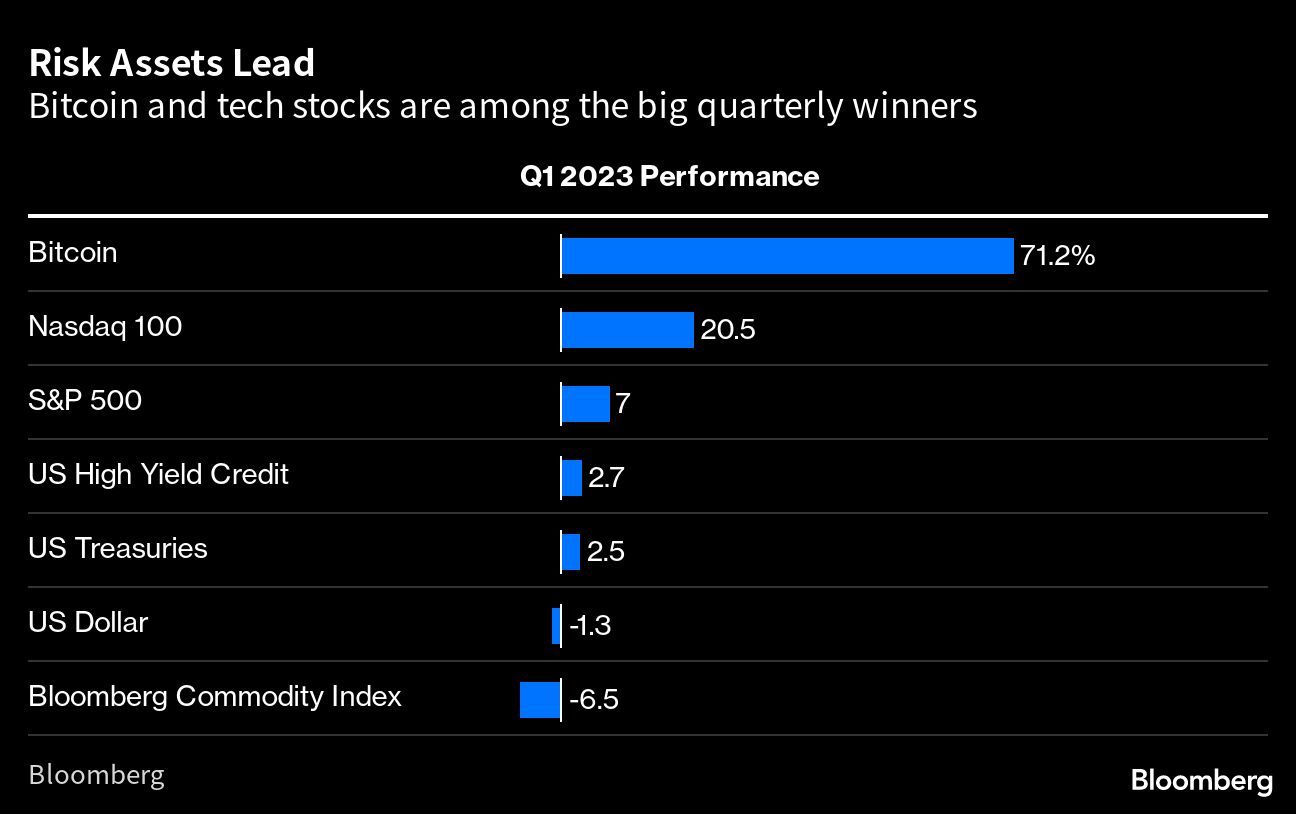
Their caution stands against a 20 per cent advance in the tech-heavy Nasdaq 100 during the first three months of this year — its best quarterly gain since 2020. Speculative fervour has also boosted the price of bitcoin by more than 70 per cent.
Markets determined to leave worries about banking sector contagion behind have put falling bond yields and rosy reads of a looser Fed balance sheet in their sights. It’s a view that directly contrasts with the latest messaging from Fed officials.
Federal Reserve Bank of Boston president Susan Collins Friday said that more needs to be done to bring inflation down, while Fed chair Jerome Powell has insisted that officials don’t anticipate cutting rates any time soon.
Article content This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content Markets have priced in a sanguine scenario where cooling inflation triggers 60 basis points of rate cuts by the end of the year. The two-year breakeven rate, a measure of the market’s inflation expectations, is hovering closer to the Fed’s target than before the banking turmoil.
The argument that easing inflation will allow the Fed to wind down its rate-hiking cycle was helped by a report on April 1 showing U.S. inflation rose last month by less than expected and consumer spending stabilized.
Still, such priced-for-perfection sentiment can quickly turn around. At a gathering of economists by Lake Como in Italy this week, Nouriel Roubini, chairman of Roubini Macro Associates LLC, summed it up: “We cannot achieve price stability, maintain economic growth, have financial stability at the same time.”
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content Fund flows underscore jitters about the risk rally. Investors flocked to cash with US$60 billion entering money market funds while they withdrew US$5.2 billion from global equity funds in the week through Wednesday, according to Bank of America Corp., citing EPFR Global data.
For Legal & General, the turning point came when the wobbly balance sheets of U.S. regional lenders such as SVB Financial Group were exposed, and a liquidity crisis swamped Credit Suisse Group AG.
The full impact of the Fed’s aggressive rate increases has yet to be fully absorbed by the American economy, warned John Roe, the head of multi-asset funds at Legal & General. He’s both cut his exposure to equities and added recession hedges in the form of long-duration government bonds.
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content “There’s never only one cockroach,” Roe said. “The SVB case isn’t isolated. It’s about the growing risk that the hikes so far in the end restrict lending — the standard lagged effect of monetary tightening.”
While Wall Street strategists haven’t changed their year-end targets, both systematic and discretionary managers have decreased exposure rapidly since March 8. The equity exposure of systematic investors fell to the lowest since 2021 as trend-following quants were caught in wild swings of the early days of the banking turmoil. Discretionary funds have now cut back exposure to underweight after hovering close to neutral levels at the beginning of March, according to Deutsche Bank.
“Our positioning measure had fallen from near neutral when the SVB shock hit to about half-way back to the bottom of the historical band,” Parag Thatte, a Deutsche Bank strategist, said.
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content Meanwhile, Fed officials continue to push back on the pivot narrative and have reiterated that more monetary tightening may be needed to fight inflation even after the collapse of three U.S. banks earlier this month. Echoing Boston’s Collins, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond president Thomas Barkin sees room for rate increases if price pressures persist.
It’s not the first time traders have been caught in wrong-way bets that rate cuts would start earlier than indicated by the Fed. In August, traders rushed to buy duration-heavy assets, convinced that an economic slowdown would bring disinflation. Since then, the Fed has raised its benchmark rate in five consecutive meetings. BlackRock Investment Institute strategists warned this week investors are wrong to believe U.S. rate cuts are coming.
This advertisement has not loaded yet, but your article continues below.
Article content Market volatility making your head spin? Here are 4 things to remember Investors take heed, corporate profit estimates are far too optimistic Why do investors always fall for the folly of forecasting? A recession should in theory vanquish inflation, but that’s not a given. In the 1970s, the Fed eased policy only to watch as inflation ran rampant and growth flatlined.
“Looking at the price action across asset classes over the last fortnight, the inference seems to be a Goldilocks growth hit for the stock market,” Hobbs said. “Something a bit more difficult to square so neatly feels more likely.”
—With assistance from Alice Atkins.
Bloomberg.com